Credentialing in medical billing is crucial for ensuring patient safety and maintaining the quality of care provided by healthcare providers. This process involves verifying providers’ qualifications, competence, and eligibility, playing a vital role in effective revenue cycle management.
In 2021, the Credential Management Solutions Market had a valuation of USD 833.45 Million. Projections indicate that it is expected to reach USD 2526.34 Million by 2030, experiencing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 17.7% from 2022 to 2030. The rising cyber threat risk has spurred demand for skilled experts, credential management solutions, and IT security compliance software in businesses and organizations. (Credential Management Solutions Market Size, Share, Trends & Forecast, 2023)
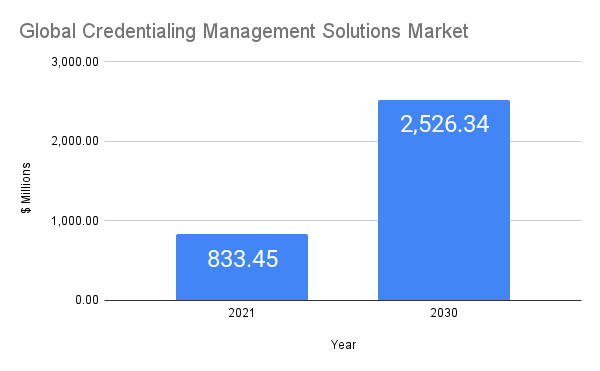
Figure 1. Global Credentialing Management Solutions Market
Medical Billing Systems in Credentialing
Medical billing systems are critical components of healthcare operations. They are used to submit and follow up on claims with health insurance companies to receive payment for services rendered by a healthcare provider. The role of medical billing systems in credentialing is quite significant.
- Provider Information: Medical billing systems hold essential information about providers, including their credentials. This information is necessary for filing claims and verifying a provider’s ability to provide certain services.
- Claims Processing: One of the key steps in processing medical claims involves verifying the provider’s credentials. If a provider is not properly credentialed with a particular payer, claims for services rendered can be denied, resulting in lost revenue.
- Regulatory Compliance: Medical billing systems help maintain compliance with healthcare regulations, including credentialing-related ones. By ensuring providers are credentialed properly, the systems help prevent fraudulent claims and avoid potential legal issues.
Integrating credentialing into medical billing systems can streamline workflows, improve accuracy, and increase efficiency. The integration can occur in various ways:
- Data Sharing: Medical billing systems can be configured to share data with credentialing systems, allowing for real-time updates of provider information.
- Automated Verifications: With the integration, systems can automatically verify a provider’s credentials during claim processing, flagging any issues for immediate attention.
- Credentialing Updates: Updates to a provider’s credentials can be automatically reflected in the billing system, reducing the chance of claim denials due to outdated credential information.
- Scheduling and Alerts: Medical billing systems can help manage credentialing timelines, offering reminders when it’s time for providers to renew their credentials, thus maintaining their eligibility with payers.
Key Facts about Credentialing Applications
Credentialing applications in the US healthcare system involve a significant volume of submissions. However, the success rate varies, with some applications failing to meet the requirements. The timeline for the credentialing process typically spans around 90-120 days, including the verification and contracting phases; per provider, there are 18 payers. For every 5 payer applications, 25 working hours of the hospital staff and physicians are consumed. Also, approximately 85% of the applications still need to be completed. (Shah, 2023)
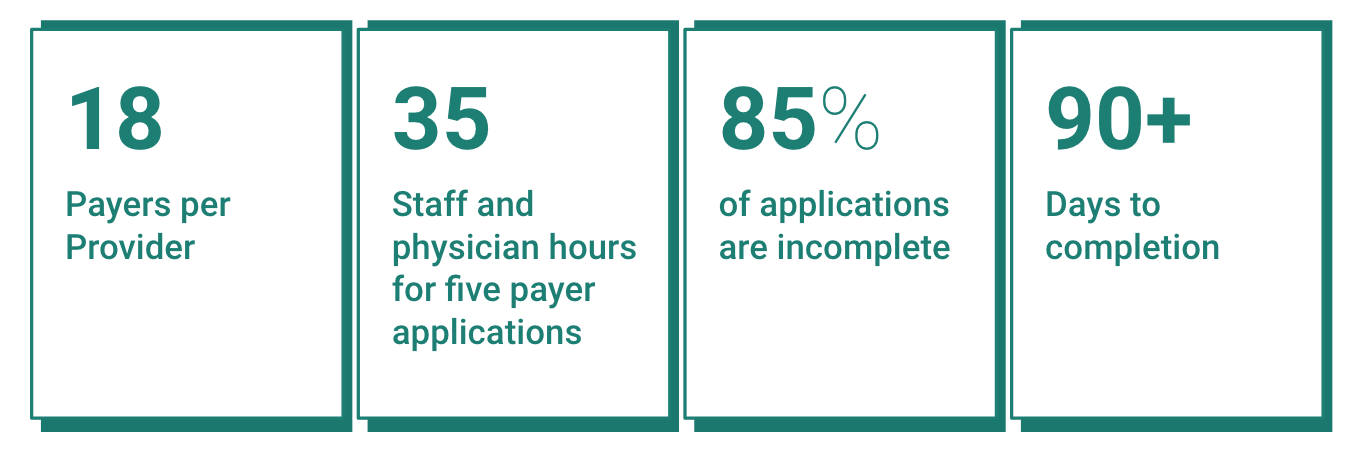
Figure 2. Basic Credentialing Facts
Challenges in the Credentialing Process
Incomplete or Inaccurate Documentation
Incomplete or inaccurate documentation is a common challenge in the credentialing process. Thoroughly reviewing the application materials and seeking assistance, if needed, can help mitigate this challenge. Maintain clear records of all documentation submitted and maintain copies for reference and future updates.
Insufficient Qualifications
Meeting specific qualifications, such as experience, licenses, certifications, or exam scores, is crucial for successful credentialing. Regularly reviewing and updating qualifications, participating in continuing education, and seeking professional development opportunities help providers stay current and fulfill credentialing requirements.
Lack of Adherence to Credentialing Standards
Adhering to credentialing standards is essential for a smooth credentialing process. Familiarize themselves with the specific standards and ensure they comply with professional conduct, ethical behavior, and patient safety requirements. Regularly reviewing the credentialing standards and seeking ongoing education on changes or updates to these standards promote ongoing compliance and avoid potential challenges.
Inadequate Professional References
Successful credentialing requires credible professional references highlighting the provider’s skills, knowledge, and abilities. Establish professional relationships and seek references from respected individuals who can vouch for their qualifications and competence. Engage in professional networks to facilitate the collection of robust references.
Disciplinary Actions or Malpractice History
Providers with a history of disciplinary actions or malpractice may face challenges during credentialing. Credentialing organizations are concerned about the provider’s competence and safety. Prepare to address any disciplinary or malpractice history concerns and provide explanations or evidence of corrective actions. Seeking legal counsel or assistance from credentialing experts can help providers navigate these challenges effectively. (Shah, 2023b)
Common Documents and Information Required for Credentialing Applications
Typically, credentialing applications include:
- Educational Background and Training Documentation: Healthcare providers must submit comprehensive documentation that validates their educational background and training. This includes transcripts, diplomas, degrees, and records of specialized training, fellowships, and continuing education courses. Accuracy in these documents is crucial as they reflect the provider’s expertise in their specific field of practice.
- Licensure and Certification Details: Credentialing applications typically seek information about the provider’s current and past licensure status. This encompasses their medical license, board certifications, and any history of disciplinary actions or license restrictions.
- Malpractice History and Insurance Coverage: Disclosure of malpractice history, including any claims, settlements, or judgments, is standard procedure in credentialing applications. This information helps assess the provider’s risk profile and ability to deliver safe, high-quality care. Providers must also furnish proof of malpractice insurance coverage or alternative means of financial responsibility.
- Professional References and Recommendations: Credentialing applications often require professional references from colleagues, supervisors, or others familiar with the provider’s clinical practice. These references offer insights into the provider’s professional conduct, clinical skills, and teamwork abilities. Recommendations from respected professionals carry significant weight in the credentialing process and positively impact the provider’s application.
- Practitioner Data Bank and National Provider Identifier (NPI) Registration: Providers are obliged to disclose any adverse actions or reportable events as required by the National Practitioner Data Bank (NPDB). This includes malpractice settlements, disciplinary actions, or exclusions from federal healthcare programs. Additionally, providers must obtain a National Provider Identifier (NPI) and include it in their credentialing application. The NPI standardizes provider identification across healthcare systems and ensures accurate tracking of provider activities. (Bhatnagar, 2023)

Figure 3. Physician Credentialing Checklist https://neolytix.com/physician-credentialing-checklist/
The Process of Credentialing
The credentialing process can be categorized into pre-credentialing, the core credentialing process, and the post-credentialing steps. Each phase plays a distinct role, from the initial preparation and gathering of documents through the rigorous review and verification steps, to the ongoing monitoring and updating of provider information. (Provider Enrollment and Credentialing, 2023)
1. Pre-credentialing Steps
Pre-credentialing is a preparatory credentialing phase. It involves several steps:
- Data Collection – The healthcare provider or their designated team collects necessary documents such as copies of licensure, certification, curriculum vitae, professional references, malpractice history, and other relevant materials.
- Initial Application – An application is prepared based on the collected data. This application typically includes personal information, educational background, employment history, and details of any past or pending malpractice claims.
- Application Submission – The completed application and all required documentation are submitted to the credentialing body. Ensuring all information is accurate and complete is essential to avoid delays or denial during the credentialing process.
2. Credentialing Process
The main credentialing process begins once the credentialing entity receives the application and documents. The core steps include:
- Primary Source Verification (PSV) – This is the critical phase of the credentialing process, where the information provided in the application is verified from the primary source. The credentialing entity directly checks the validity of licensure, certifications, training, and educational qualifications from the issuing bodies.
- Committee Review – Once the PSV is complete, the data is reviewed by a credentialing committee. This review process can include interviews, peer reviews, and further assessment of the provider’s capability to provide quality care. Background checks and screenings are conducted as part of credentialing to ensure provider integrity and patient safety.
- Decision Making – Once submitted, the credentialing application and supporting documents undergo a thorough review by the credentialing organization. Based on the verification results and committee review, a decision is made to grant, deny, or defer the credentialing application. If approved, the healthcare provider is added to the payer’s network.
3. Post-credentialing Steps
Post-credentialing steps are carried out once the provider has been credentialed.
- Notification – The provider is informed of the credentialing decision. In case of approval, they will receive information on their participation in the network, including the effective date.
- Updating Systems – Details of the newly credentialed provider are added to the healthcare provider’s medical billing system, enabling them to submit claims for services rendered.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Re-credentialing – Credentialing is not a one-time process. It requires periodic review and re-credentialing to ensure that healthcare providers maintain their qualifications and competency. This usually occurs every two to three years or as determined by the credentialing entity or regulatory guidelines.
- Provider Credentialing Updates – Any provider status changes, such as new certifications or a location change, should be updated promptly with the credentialing entity.
The process of credentialing can be summarised in the image below (Shah, 2023)

Figure 4. Credentialing Process Workflow
Key Considerations for Choosing the Right Credentialing Software
Credentialing software plays a crucial role in the efficient management of medical billing and provider data in healthcare organizations. When selecting the best credentialing system, several essential factors should be taken into account to ensure seamless integration, scalability, and user-friendly functionality. Below are the key considerations to look for in credentialing software:
- Integration and Migration Simplicity: An ideal credentialing system should offer seamless integration with existing software suites and allow easy migration of data. This ensures interoperability and eliminates the need for manual data input, making the process scalable and efficient.
- Cloud-based Capabilities: Opt for a cloud-based credentialing solution as it offers flexibility, scalability, and access to cloud-based resources. Such a system can handle multi-site credentialing requirements and effortlessly integrate and migrate data, enabling medical health centers to expand their operations without worrying about credentialing processes.
- Robust Document Management: Choose a credentialing system incorporating a document management system. The system should allow flexible document storage and retrieval, catering to the dynamic nature of healthcare processes. Security and privacy features should be available to control access and classify data into different categories.
- Electronic Form Automation: Look for a system that provides electronic forms to automate the form-filling process. The software should be capable of pre-populating information from various provider profiles, minimizing manual data entry. This automation streamlines the entire credentialing workflow, making it paperless and efficient.
- Customizable Workflow Systems: Ensure the credentialing software offers good and flexible workflow systems that can be fully automated. It should allow users to define their workflows through a user-friendly interface, reducing the need for coding. Customizable workflows cater to various data sets and adapt to complex use cases.
- Peer Review Functionality: Choose a credentialing system that enables peer reviews for applications, providing instantaneous feedback to medical professionals. Make sure it adheres to HIPAA compliance to ensure data privacy and security. All reviews and interventions should be tracked and logged using standardized and structured mechanisms.
- CME Tracking Module: Look for a system that offers a continuous medical education (CME) tracking module, allowing medical professionals to monitor their education requirements and plan their credentialing activities accordingly. This feature helps practitioners stay updated on the latest medical developments and assess the cost and labor involved in CME.
- Easy Implementation: Select a credentialing system with low implementation overheads, available in various provisioning options like virtual machines and containers. The platform should have self-explanatory workflows, enabling users of all skill levels to operate it with basic computer knowledge.
- Comprehensive Customer Support: Ensure the credentialing software vendor provides excellent customer support via live chat, email, or phone. A good help system, training materials, and online videos should be available to assist users in leveraging the system effectively. The vendor should also understand and accommodate customization requirements for evolving medical billing processes during the digital transformation.
Use of Advanced Technology and AI in Medical Credentialing
Automation and Streamlining of Credentialing Procedures
Advanced technology solutions centralize data, automate application processes, track credentialing statuses, and generate reports. Technology solutions enhance the credentialing process’s effectiveness by reducing manual errors, ensuring consistency, and improving efficiency. (Shah, 2023b)
Data Analytics for Continuous Improvement
Data analytics plays a crucial role in the continuous improvement and optimization of the credentialing process. By analyzing credentialing data, organizations can identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. Data analytics can help streamline workflows, reduce processing times, and identify potential bottlenecks or inefficiencies. By leveraging data analytics tools and insights, organizations can make data-driven decisions to enhance the effectiveness and efficiency of the credentialing process. (Lateef, 2023)
Blockchain Technology for Secure and Transparent Credentialing
Blockchain technology offers enhanced security and transparency in the credentialing process. By utilizing a decentralized and tamper-resistant platform, blockchain can securely store and share credentialing information. Blockchain can authenticate and verify credentials without the need for intermediaries, ensuring data integrity and privacy. The integration of blockchain technology provides a more secure and transparent credentialing ecosystem. (Council, 2023)
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Intelligent Decision-Making
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in credentialing can enhance verification accuracy, streamline workflows, and improve decision-making processes. AI and ML algorithms can analyze large datasets, identify patterns, and make intelligent predictions. These technologies can expedite the verification process, detect anomalies, and ensure compliance with credentialing standards. AI and ML solutions offer intelligent insights and automation, contributing to more efficient and effective credentialing outcomes.(Shah, 2023b)
Conclusion
Credentialing in medical billing is vital for patient safety and maintaining quality care. Integrating credentialing with advanced technology, such as AI, blockchain, and data analytics, streamlines the process and improves accuracy. This ensures efficient revenue cycle management and enables healthcare providers to deliver high-quality care to patients. Embracing these advancements will shape the future of medical billing credentialing, benefiting both providers and patients alike.
Resources:
- Credential Management Solutions Market Size, Share, Trends & Forecast. (2023, March 27). Verified Market Research. https://www.verifiedmarketresearch.com/product/global-credential-management-solutions-market-size-and-forecast-to-2025/
- Shah, R. (2023, July 26). 10 Must-Have Features in Your Healthcare Credentialing Software. Osplabs.
- Bhatnagar, R. (2023, July 28). The Most Important Physician Credentialing Checklist You’ll Ever Need. Neolytix. https://neolytix.com/physician-credentialing-checklist/
- Provider enrollment and credentialing. (2023, March 22). Access Healthcare. https://www.accesshealthcare.com/services/revenue-cycle/provider-enrollment-and-credentialing-services
- CAQH – Streamlining the business of healthcare. https://www.caqh.org/solutions/provider-data/credentialing-suite
- Lateef, Z. (2023). Implementing Artificial Intelligence In Healthcare. Edureka. https://www.edureka.co/blog/artificial-intelligence-in-healthcare/
- Council, B. (2023). Top 5 benefits of blockchain technology. Blockchain Council. https://www.blockchain-council.org/blockchain/top-5-benefits-of-blockchain-technology/
- Shah, R. (2023b). Credentialing in Medical Billing: Everything you need to know. Osplabs. https://www.osplabs.com/insights/everything-you-need-to-know-about-credentialing-in-medical-billing/










